|
|
NOTE: this topic is a key topic on the AQA and Edexcel specifications. It is NOT a stated topic on the OCR specification, but is important backgound knowledge.
|
|
[Khrushev] displayed a shocking rigidity in his thinking about the West – an apparent willingness to swallow the propaganda he himself has helped create. Marshall MacDuffie, quoted in a top secret CIA briefing paper (1955) MacDuffie was the American UNRRA representative. The CIA described him as the person who had ‘seen more of Khrushchev than any other westerner’.
As a matter of pride and profound geopolitical anxiety, Moscow wanted to be recognised as equal superpower. German historian Konrad Jarausch, The Cold War: Historiography, Memory, Representation (2017)
Stalin died in 1953. He was hated all over eastern Europe. When they heard he was dead, people in East Berlin rioted. After a short struggle for power, Khrushchev became the new ruler in Russia.
|
Did You Know?Even though he was poorly-educated and had
had a peasant up-bringing, Khrushchev had insight and a good turn of phrase. He once said that Communism and capitalism would only agree
"when shrimps learned to whistle". Khrushchev, however, was NOT a gentle easy-going man; he had been Stalin’s right-hand man – Stalin had used him to run the terror purges after World War II. *** While denouncing Joseph Stalin in a speech one day, Khrushchev was interrupted by a voice from the audience: "You were one of Stalin's colleagues," the man declared. "Why didn't you stop him?" "Who said that!?" Khrushchev roared. This was followed by a terrified silence - only broken at last by Khrushchev himself. "Now..." he said in a quiet voice, "Now you know why."
|
Peaceful Co-existenceAt first, the western powers hoped that Khrushchev would be the start of a ‘thaw’ in the Cold War.
Source AYou do not like Communism. We do not like capitalism. There is only one way out – peaceful co-existence. Khrushchev speaking on a visit to Britain in 1956.
Source BWe may argue. The main thing is to argue without using weapons. Khrushchev speaking in 1959.
Source CThe death of Stalin (1953) was probably the starting point of the 'thaw' because it brought to the forefront leaders in Russia - for example Khrushchev - who wanted to improve relations with the west... Khrushchev explained the new policy in his famous speech (February 1956) in which he criticised Stalin and said that 'peaceful co-existence' was not only possible but essential: 'there were only two ways - either peaceful co-existence or the most destructive war in history. There is no third way'... Norman Lowe, Mastering Modern World History (1982) Written as a GCSE revision book by a History teacher.
Consider:1. Look at Khrushchev's actions and comments in points 1-4 and Sources A-C. Taking each in turn, consider what might they have encouraged western leaders to conclude. 2. Using the Sources and information on this page, discuss why Khrushchev's intention of 'peaceful co-existence' failed.
|
Going Deeper
What was Khrushchev Up To? - my ideas on the dilemma of Khrushchev's 'mixed messages' Khrushchev – friend or foe? - an exercise/checklist
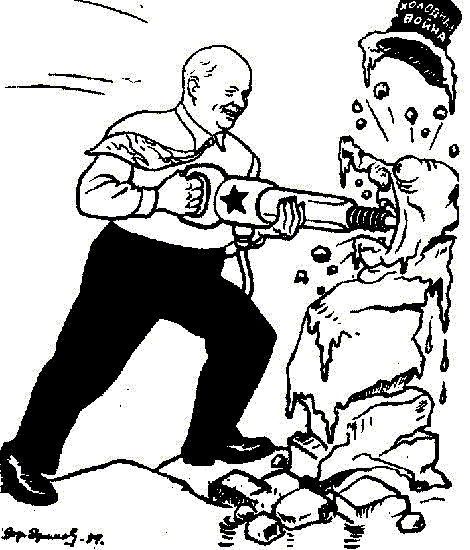
Source D
This Russian cartoon shows Khrushchev destroying the snowman (representing the Cold War). Click here for the interpretation
Did You Know?
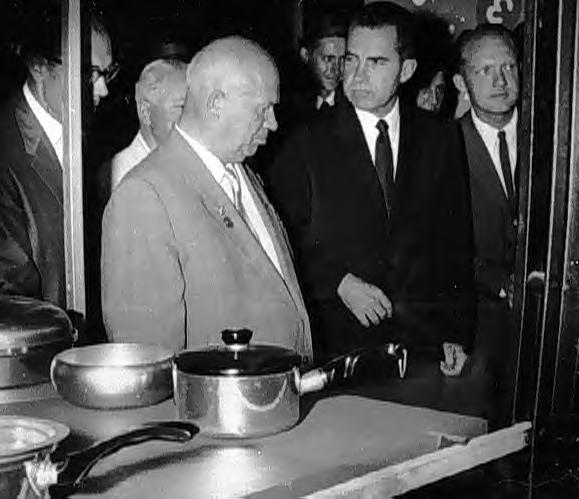
Khrushchev loved to argue, which sometimes increased tension. When American Vice-President Nixon visited Russia in 1959, he was taken round an exhibition at the US Trade Fair. At the kitchen display, he and Khrushchev had a public argument - the so-called 'Kitchen Debate' - about who had the better kitchens: communism or capitalism!
|
Increasing TensionIf the rulers of the West hoped that Khrushchev would bring an end to the Cold War, they were disappointed: ‘De-stalinisation’ did not mean a change back to capitalism, or freedom from Russia; when communist countries went too far in their reforms, Khrushchev sent in the Red Army to stop them. And by ‘peaceful co-existence’, Khrushchev really meant ‘peaceful competition’. He started to build up Russian power:
Faced by this, America became just as aggressive:
As a result, the period 1955–1963 was a time of GREAT TENSION in the Cold War. Source EThe 'thaw' was only partial: Khrushchev's policy was a curious mixture which western leaders often found difficult to understand [and] he was quick to respond to anything which seemed to be a threat to the east. From a GCSE revision book Written by a History teacher (1988).
Source FAlthough Khrushchev has been careful to pay lip service to the coexistence theme, this has apparently meant for him little more than an absence of armed conflict. In a speech in Prague in June 1954, he stressed Soviet possession of the atom and hydrogen bombs, as well as the necessity for maintaining and increasing Soviet armed strength. Several times he referred to the West as ‘the enemy’ and spoke of capitalist encirclement… On 10 August … he indicated that there could be trade and increased diplomatic intercourse, but no change in ideology, thereby implying no respite from political warfare. [When pressed] Khrushchev blurted, ‘In this field there can be no coexistence’. Analysis of Khrushchev's views in a top secret CIA briefing paper (September 1955)
|
FIVE Crises after 1955:1956 Poland 1956 Hungary 1960 U-2 crisis 1961 The Berlin Wall 1962 Cuban Missile Crisis
EIGHT Countries in the Warsaw Pact:• USSR • Albania • Bulgaria • Czechoslovakia • East Germany • Hungary • Poland • Romania
In the 1950s and 60s many US films showed fear of Communism; the most famous was Red Menace (1949), a film about Communists taking over America.
The film Them! (1954) was an allegory of the cold war, teaching Americans to hate 'the enemy'.
Get Smart was a hilarious spoof TV for children which imagined an outside force trying to reduce society to KAOS.
Neville Shute's novel On the Beach (1957) imagined a group of people waiting to die after a nuclear holocaust.
|
Source G
This 1961 cartoon shows America and Russia at loggerheads with each other. Most people expected that a nuclear war would happen - the atom bomb affected modern life and culture?. Both the British and US governments have out public advice on what to do in the event of a nuclear attack, and American children were trained what to do in the event of a nuclear strike - 'Duck and Cover'.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Spotted an error on this page? Broken link? Anything missing? Let me know. |
|